eBook
The Winning Formula for Your ISO 20022 Payments Migration

Is Your Business Ready for ISO 20022 Payments Migration?
The lack of payment messaging standards around the globe has been a major issue for payment factory or payment hub modernization. The absence of standards has resulted in expensive cross-border payments, insufficient transparency, increased fraud, and heightened security risks. Many companies have allocated extensive resources to develop local formats, yet still face a complexity that prevents them from harmonizing end-to-end processes, including payments validation and data reconciliation, for domestic and international transfers.
Over the years, the adoption of the 2009 version of the ISO 20022 XML messaging standard has represented great progress. It is considered a mature format that is important for corporate payments globally. Nevertheless, companies and banks are still spending a lot of time and money supporting and maintaining local legacy formats–or even worse, proprietary formats–that pose maintenance challenges on a daily basis.
Fortunately, under the joint effort of SWIFT, the European Policy Center (EPC), as well as many banks and corporations, the 2019 version of the ISO 20022 XML messaging standard could be the light at the end of the tunnel.
Table of Contents
- What’s New in the Latest Version of the ISO 20022 XML?
- Why is ISO 20022 Important to ERP-to-Bank Connectivity & Payments?
- What Does it Mean for Your Organization?
- Cleaning up the ERP Database with More Structured Third-Party Information.
- Harmonizing the Payments Validation Workflow.
- Creating Processes for ERP and TMS Integration and Automating End-to-end Reconciliation.
- How Can a Technology Partner Help?
- References
- Sources
What’s New in the Latest Version of the ISO 20022 XML?
ISO 20022, first introduced in 2004, is a messaging standard that establishes a common digital language for financial data worldwide. While SWIFT has started the migration towards ISO 20022 XML messages, the standard is widely used beyond SWIFT services. Currently, most real-time payments systems are using ISO 20022, and the standard has been used for more than 10 years for SEPA Credit Transfer and Direct Debit. Additionally, ISO 20022 is used for invoicing, investment fund orders, and foreign exchange activities.

ISO 20022 contains many messages and it also has yearly releases. For instance, ISO 20022 release 2009 contains the pain.001.001.03 message, the most commonly used messaging format for payment initiation. In ISO 20022 release 2019, which is the latest version, the same message has been upgraded to version 09, pain.001.001.09.
When it gets adopted by a majority of organizations, the 2019 version of the ISO 20022 XML messaging standard will allow for speedy payment transactions, in part because it would eliminate complex layers of legacy payment codes.
By November 2025, SWIFT messages will be fully transitioned to ISO 20022 XML for interbank settlements. For this migration, most banks will change their infrastructure and therefore will push their corporate clients to adopt the 2019 version of the ISO 20022 XML over other local standards for payments, such as DTAZV in Germany and AFB320 in France. The process has already started in Switzerland, where SIX is promoting this format as the new Swiss standard and Credit Suisse and the Swiss National Bank are already making it available to their customers.
In Europe, the EPC has announced that the new version will become the SEPA Credit Transfer format as soon as November 2023. Common Global Implementation (CGI), an initiative to simplify various payment related corporate-to-bank implementations by promoting the wider acceptance of ISO 20022 XML, has already released its specifications.
Globally, this new standard will allow the transmission of rich data in a more structured manner. It will enable end-to-end tracking and reconciliation of payments, which has always been an issue with cross-border payments. Currently, over 70 countries are already in the process of adopting ISO 20022, including China, India, and Japan.

Why is ISO 20022 Important to ERP-to-Bank Connectivity & Payments?
With the imminent global adoption of the 2019 version of the ISO 20022 XML, organizations need to be aware of its benefits as well as its limitations, as they prepare to add it to their payment mix.
For finance and IT leaders, the new standard offers a myriad of benefits in comparison to its predecessors. Adopting ISO 20022 standards helps to prevent fraud, avoid system failures, and expedite payment transactions, large and small.
Use case highlights:
- Instant Payments: The standard enables frictionless, real-time payments by creating a global, open standard that anyone can implement on any network.
- Rich Data: The rich, consistent, well-structured data enabled by the new standard delivers faster transactions and helps drive innovation by allowing organizations to develop products based on customer needs.
- Improved Regulatory Reporting: Because the new standard requires identical formats and a higher level of detail, it creates more secure payment information that lends itself to better, faster regulatory reporting.
- Fraud Prevention: A standard payment format helps organizations identify fraud, including money laundering. The fact that the new format requires structured and complete addresses limits the fraud risks too.
- Compliance (Security Enhanced): The consistent payment format facilitates compliance with government regulatory requirements.
- Interoperability: The standard helps to promote interoperability for cross-border payments, improving the ability to easily exchange and make use of information.
- Payments Hub Upgrade: It meets the need for payment system renewal programs, ensuring alignment with global industry standardization such as SWIFT’s cross-border payments messaging migration where the MT messages will gradually be replaced by XML.
- Faster Reconciliation: It supports Unique End-to-end Transaction Reference (UETR) with a standardized tag, allowing the transmission of this unique id from any ERP system in a payment file to the bank and back in payment acknowledgement and bank statements.
- Tracking and Beneficiary Advice: The new standard improves the transmission of information through end-to-end tracking and the payment advice to the final recipients.
On the flip side, while the new standard promises improved messaging interoperability between systems for the greatest number of participants, the actual experience is dependent on how individual banks set up the messaging standard internally. In other words, banks will deploy the new messaging standard differently and some workarounds will likely be necessary for seamless payment transactions.
What Does it Mean for Your Organization?
With so many tangible benefits the new standard can bring to the corporate payments, organizations should adopt it as soon as their banking partners offer it. However, according to a recent Celent survey, not all banks are equally prepared for ISO 20022 migration. As a result, Celent also found that many corporate clients have not been sufficiently informed by their banking partners on the forthcoming ISO 20022 changes and more importantly, what actions companies would need to take to plan for the changes.
Banks* indicate time, resource, and technology constraints as major hurdles to their ISO 20022 migration.

73 percent of banks agree that technology constraints within the bank limit their ability to do more with their migration to ISO 20022.
63 percent of banks agree that budget or resource constraints limit their ability to do more with their ISO 20022 migration.
Celent anticipates that the majority of banks will do just enough and be largely on time for the deadline.
* Data from 51 banks surveyed across Europe
Source: CELENT (2022). Survey & report: The race to ISO 20022.
This lack of communication is unfortunate as corporations must also prepare their systems to send and receive the new payment format. If not, the opportunity to benefit from the richer data is lost because the extensive data in payment messages could be truncated by the end recipient due to system unreadiness and messaging incompatibility.
Based on Kyriba’s experience, we foresee that it will require some effort for enterprises to get their internal systems ready for the new message format. A quick checklist includes:
Cleaning up the ERP Database with More Structured Third-Party Information.
As more and more countries will only allow structured addresses in cross border transfers, complete information for the beneficiaries (full names, complete addresses and even identification numbers) will become a must. SWIFT initiative, known as CBPR+ (Cross Border Payment and Reporting +), aims to provide structured addresses already in MT messages. Kyriba advised its clients to start completing the structured addresses, at least for city, zip code, and country (and for some countries, also state/province).
Harmonizing the Payments Validation Workflow.
As part of the workflow design, Kyriba’s recommendation to our clients is to consider implementing a fraud detection system. The rule-based and AI-powered fraud and compliance detection mechanism will remove a lot of time-consuming and error-prone manual steps to validate payments and let all stakeholders get better control over the payments processed.
Creating Processes for ERP and TMS Integration and Automating End-to-end Reconciliation.
By using a unique import interface, generating unique ids for each imported file, and initiating payments in formats containing these unique ids, the reconciliation process will be transformed. Acknowledgments will be integrated with a specific format (XML Pain.002.001.10) that will allow cash managers to be alerted almost immediately when a payment is rejected. With end-to-end integration, the information can be fed in real time back to ERP for quick action.
How Can a Technology Partner Help?
After years of working with dedication to create a vast library of proprietary formats, the Kyriba payments team sees the coming changes as a chance to get closer to global standardization. However, as a mission-critical process, any disturbance in payment processes could cause business disruption, supplier dissatisfaction, and late material deliveries. Understandably any major format change or update makes payments and IT teams apprehensive. Therefore, it pays off to understand the subject matter in advance, plan a progressive roadmap to adopt the new standard, and if needed, work with a specialist vendor to manage the whole transformation.
Kyriba is always at the forefront of formats and payments innovation, with proven ability to quickly support the latest formats required by the market. Kyriba clients can already seamlessly exchange payment transaction data with Credit Suisse using the new standard. Kyriba also supports SEPA CT XML ISO 20022 version 2019, has developed the CGI standard version XML ISO 20022 version 2019 format, and is ready to support the SWIFT migration from MT to MX messages via SWIFT Interact.
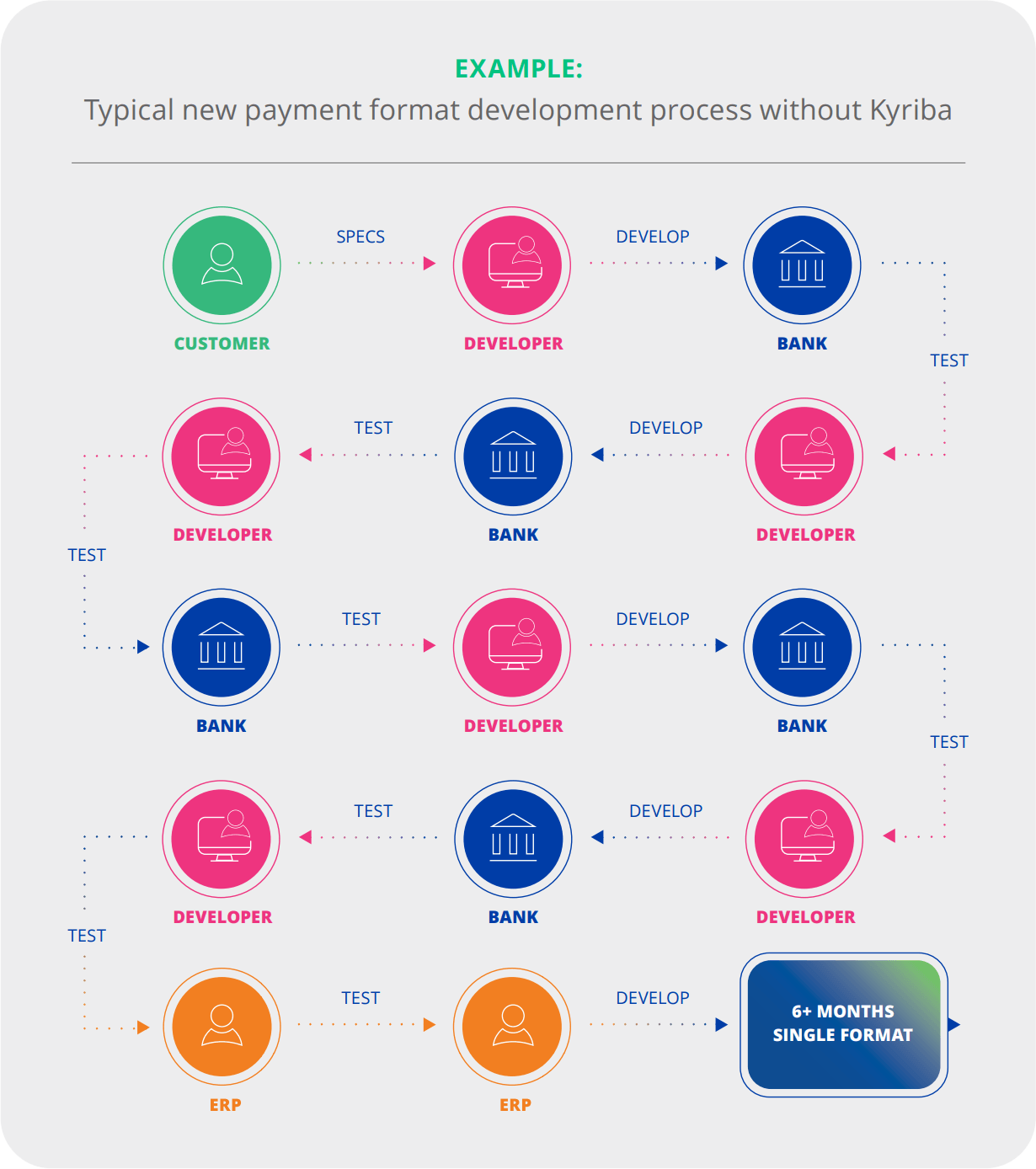
To illustrate the efforts it usually takes to develop payment templates, let’s deep dive into the process:
- All payment templates must be individually developed and tested with each bank
- Developers must coordinate all testing with each bank’s technical team
- Format typically fails first test, multiple rounds of testing are required with each format
- Companies must work on each bank’s timeline and time zone
- Average timeline from development to production is 3-6 months for a single payment format
Kyriba offers its clients a pre-built and pre-tested payment format library with over 50,000 payment scenarios ready for use, covering all major banks across the globe. Based on Kyriba’s Value Engineering Projects with our clients, Kyriba clients are looking at an average saving of $100,000 from this time-consuming and labor-intensive process.
References
- Common Global Implementation (CGI) Initiative
- European Payments Council (2022): Guidance on the Migration to the 2019 Version of the ISO 20022-based XML Messaging Standard
- ISO (2020) Introduction to ISO 20022: Universal Financial Industry Message Scheme
- SWIFT (2022) UETR
- SWIFT (2022) What is ISO 20022?
Sources
- CELENT (2022) Survey & Report: The Race to ISO 20022
- The SWIFT Standards Team (2020): ISO 20022 for Dummies (5th) John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Watch our on-demand webinar to learn more about Beam Suntory’s treasury and payments transformation journey, including using the Kyriba Payment Hub for auto converting ISO 20022 XML format.









