FAQ
What is Connectivity-as-a-Service?

Connectivity-as-a-Service (CaaS), or corporate ERP to bank connectivity as a service in treasury and corporate payments management, is to provide quick onboarding and secure connectivity services to businesses so that they can be released from the workload of building and maintaining those connectors by themselves with cost efficiency.
By choosing Connectivity-as-a-Service, organizations can reduce time spent on connecting ERPs to banks by as much as 80%, compared to the DIY approach. The main reason is that in today’s corporations, it is very common to build or buy a special-purpose software or a Software-as-a-Service platform in order to digitize a particular business process, treasury being one of them. Along with many of such digitalization initiatives over the years comes the challenge of system silos.
Moreover, as the number of systems grows, so does the architectural complexity behind them. A by-product of such IT infrastructure growth is the lack of connectivity among different systems. From ERP to CRM to TMS, manual data transfers are still unavoidable, leading to inefficiency, inaccuracy, and insecurity in corporate information management.
Version control is another issue. Even with the same software vendor, different versions of software may not be able to integrate without a significant upgrade, which requires IT resources. S/4HAHA migration is a good example.
The assessment of migrating existing bank connectivity to the new cloud and the difficulty of adding successive banks is typically one of the most underestimated areas of the project. When multiplied across a dozen partner banks, with their own flavor or proprietary requirements and connectivity standards, durations extend accordingly.
Table of Contents
Connectivity needs in Corporate Treasury
Depending on the scale of a corporate, usually there are the following needs for connectivity in corporate treasury:
- Bank connectivity: usually this is required for corporate payments, bank relationship management, bank account management, or compliance. Bank connectivity in modern enterprises is usually done by host-to-host FTP, API or SWIFT.
- ERP-to-bank connectivity: recently the term ‘Embedded Treasury’ has captured a lot of attention from treasurers. In essence it means to embed banking data and payment processes into ERPs to achieve a new level of system integration and data accessibility. This can be achieved by using prebuilt ERP connectors.
- Open API connectivity: many system vendors today provide a suite of open API to facilitate system integration or use case innovation. By using open API companies can enhance their financial processes with less software development effort. Meanwhile, the processes can be extended to include more data points for better decision making.
For example, treasury and FP&A under the office of the CFO can easily connect their systems through open API integration provided by the vendors and achieve new levels of data sharing.
Kyriba recently partnered up with Acterys, a unified SaaS platform for analytical applications suited for financial reporting, consolidation, and planning solutions integrated with Power BI & Excel. Together the two companies are ready to support the CFO office to combine strategic analysis with operational missions to produce more accurate forecasts and predictions.
Challenges with ERP to Bank Connectivity in Corporate Treasury
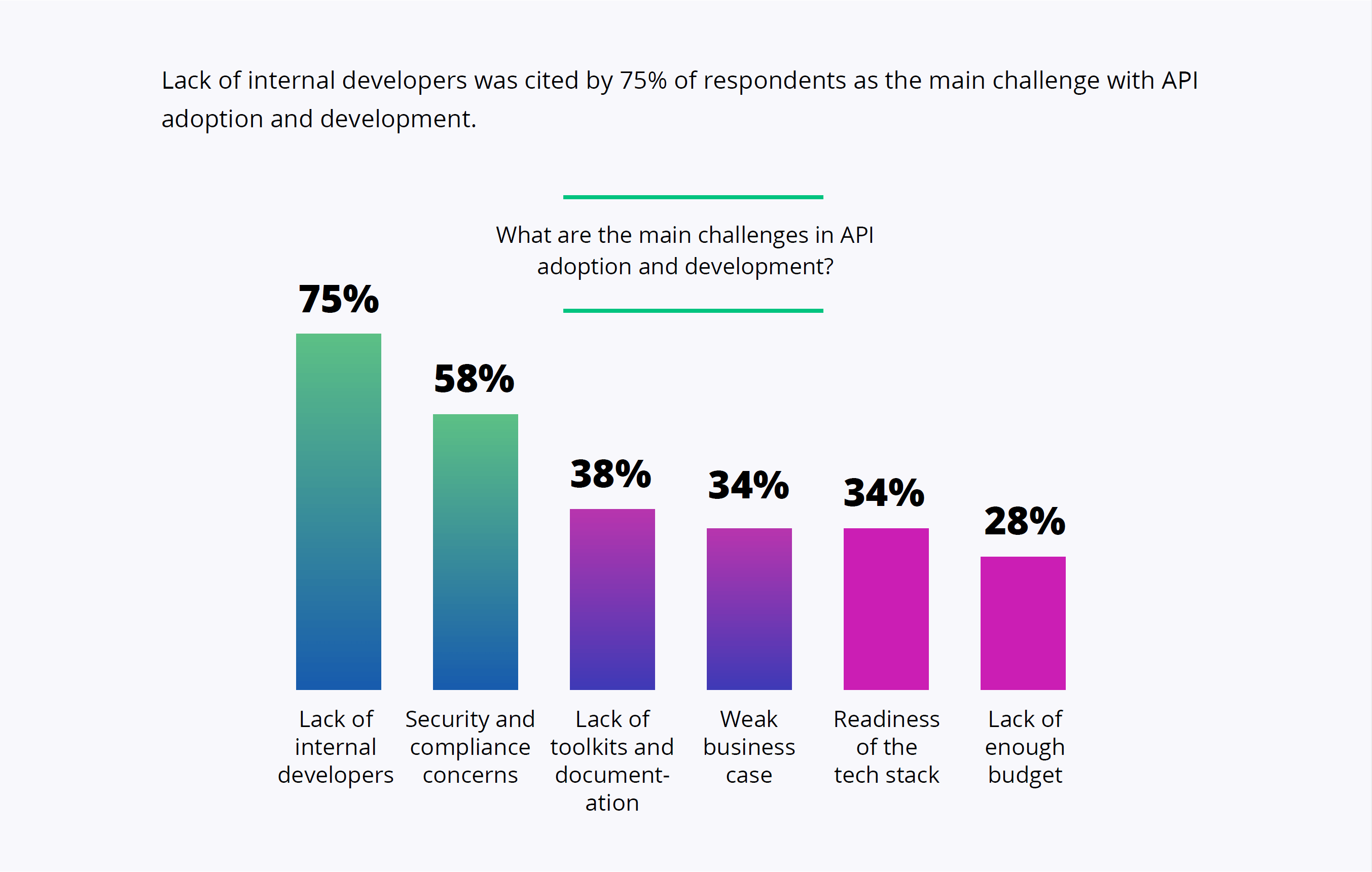
From several surveys conducted by Kyriba and Gartner Peer Insights on the topic of connectivity among CIOs, the following challenges are shared across corporates in different industries:
- Resourcing, both in terms of budget and IT talent
- Meeting the required timeline for new system implementation or the migration of old systems
- Maintenance of the legacy systems which cannot easily be retired or replaced by new systems
- Connecting treasury or other payment systems to multiple banks with different specifications and payment formats
- Lack of standardization across system interfaces or lack of interoperability
- Cyber security, compliance, and growing threshold for privacy and data protection
Find out more on the main research questions and the results of the surveys:
- What impacts do IT leaders expect APIs to have now and in the future? Survey: APIs-Enterprise Maturity and Use Cases
- What are the key considerations when IT leaders form their strategy and roadmap? Survey: IT Priorities and Technology Selection
What Are the Benefits of Using Connectivity-as-a-Service?
Taking into consideration the challenges and the amount of resources required to tackle them, many companies have chosen to work with a technology vendor who specializes in providing Connectivity-as-a-Service.
The main benefits of working with a vendor include:
- Leverage preconfigured and pretested connectors for ERP to Bank connectivity. Companies use mainstream ERP systems such as SAP, D365, Oracle, or Netsuite do not have to build all these connectors one by one. Instead, they can leverage the pre-built and pre-tested bank connectivity solutions.
- Use the latest connectivity options such as Bank APIs and other ad hoc connectors. At Kyriba’s Marketplace, you can already find 15 real-time bank connectivity solutions to all major banks, supporting use cases of payments, statements, and transactions.
- Dramatically decrease the time and costs associated with system migration or maintenance.
- Minimize system maintenance costs by outsourcing it to technology partners
- Improve end-to-end automation and quality of data for better decision-making
- Focus IT staff productivity on initiatives driving top-line business growth
ROI of Choosing Connectivity-as-a-Service
Kyriba’s Value Engineering team works closely with our clients to understand how value has been realized by choosing Kyriba’s products and services.
Based on Kyriba’s experience working with our clients who have various connectivity needs and the use of state-of-the-art tools and processes to evaluate the return on investment, our conclusion is that the choice to use Connectivity-as-a-Service generates tangible return on the initial investment our clients make.
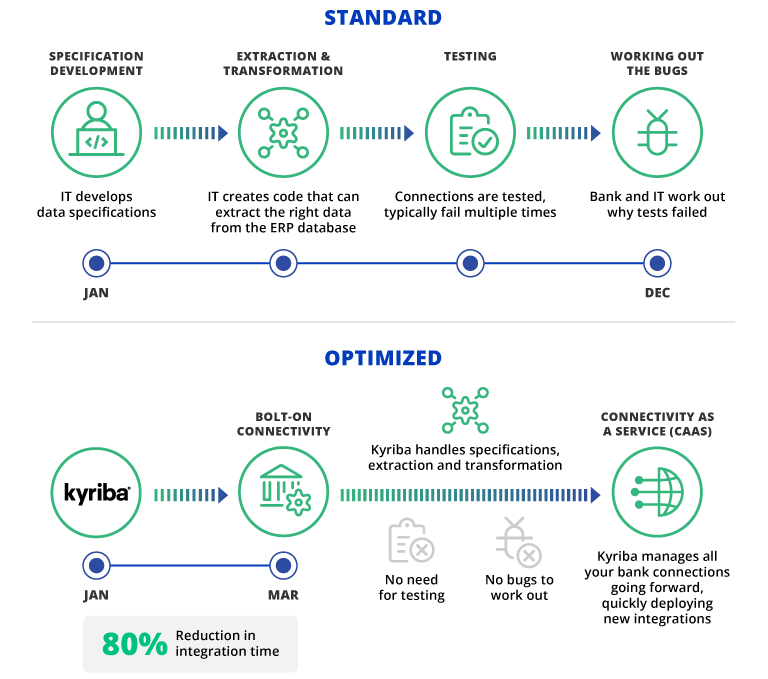
Below is a simple comparison to demonstrate how up to 80% reduction in integration time can be achieved by clients who choose to use Kyriba to connect to their banks instead of doing it by themselves.
Examples of Using Connectivity-as-a-Service
No two companies have the same IT set-up. There are many ways to start the use of Connectivity-as-a-Service. Below are a few examples from the success stories achieved by Kyriba clients.
Case 1: Kyriba client Oracle Cerner chose to migrate its SWIFT BIC to the SWIFT Service Bureau offered by Kyriba. By using this Connectivity-as-a-Service for SWIFT bank connectivity, Oracle Cerner can comply with SWIFT standards and save costs of maintaining SWIFT AL2.
- Outcome: the company saved 930 IT hours per year, including 410 hours of SWIFT AL2 maintenance and 520 hours of bank connectivity maintenance.
Case 2: Kyriba client Adobe has 125 global users manually logging into 10+ banking portals on a daily basis to process payments and statements. By choosing Kyriba’s Connectivity-as-a-Service for bank connectivity, Adobe has achieved:
- Centralized repository of 24 signers tracked and 8 bank letter templates maintained
- 4 Banks connected for bank fee statement reporting and proactive fee management
- FBAR reporting information generated from Kyriba
Case 3: Kyriba client Şişecam uses Kyriba’s Connectivity-as-a-Service for ERP to bank connectivity to ensure that all payment orders have to be raised via Şişecam’s ERP systems. If there is no record of a payment order in an ERP system, that payment will not be made.
- Workflow: Once an order has been raised on an ERP system, a payment file is created directly within Kyriba. Signatories can log in to the system to approve payments quickly and easily, using multi-factor authentication security, before the payment request will be sent out to the banks for further processing.









